Operating Principles of Sulfuric Acid Plants
Sulfuric acid is a strong and highly corrosive acid that is widely used in a variety of industrial processes. It is produced by the sulfuric acid process, which involves the reaction of sulfur dioxide with oxygen to produce sulfur trioxide, which is then absorbed in a solution of water to produce sulfuric acid.
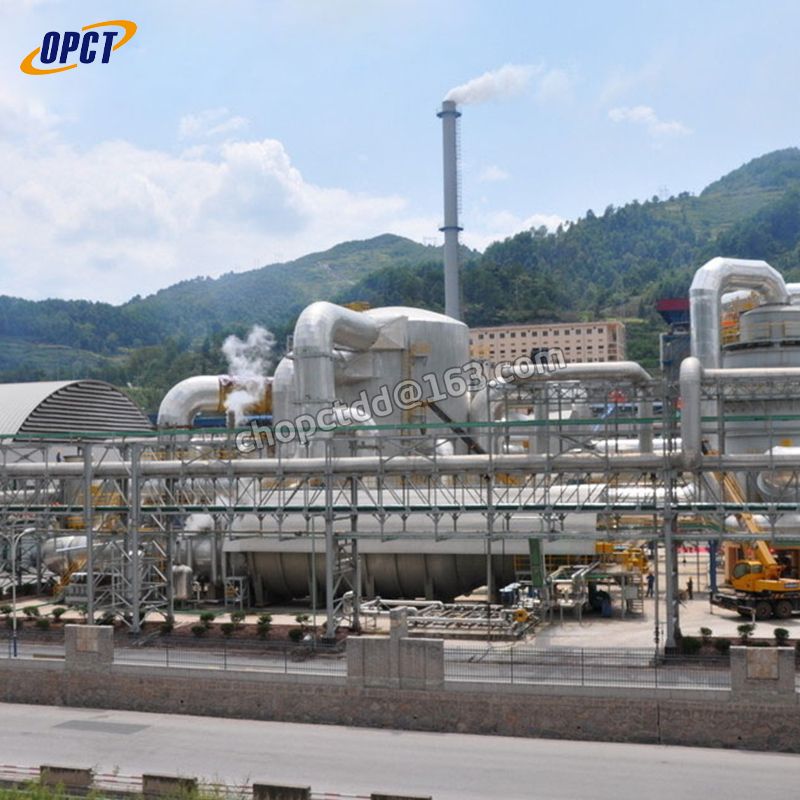

There Are Several Principles That Are Used in the Design and Operation of a Sulfuric Acid Plant:
1. Chemical reactions: The sulfuric acid process involves several chemical reactions that must be carefully controlled in order to produce high-quality sulfuric acid. These reactions include the burning of sulfur to produce sulfur dioxide, the oxidation of sulfur dioxide to produce sulfur trioxide, and the absorption of sulfur trioxide in water to produce sulfuric acid.
2. Heat transfer: The sulfuric acid process is exothermic, meaning that it generates heat as a byproduct of the chemical reactions that take place. This heat must be properly managed in order to maintain the temperature and pressure conditions needed for the reactions to occur.
3. Mass transfer: In order for the chemical reactions in a sulfuric acid plant to occur efficiently, the reactants must be properly mixed and transported within the plant. This is accomplished through a combination of mechanical mixing and the use of specialized equipment such as scrubbers and absorbers.
4. Process control: The operation of a sulfuric acid plant requires careful control of various process variables such as temperature, pressure, flow rate, and chemical composition. This is typically achieved through the use of automated control systems and sensors that monitor key parameters and adjust the process accordingly.
5. Safety: Sulfuric acid is a highly corrosive and potentially dangerous chemical, and the operation of a sulfuric acid plant requires strict adherence to safety protocols in order to prevent accidents and minimize the risk of injury to workers.
For more information, please contact us. We will provide professional answers.