Preparation of Sulphuric Acid by Contact process
Preparation of Sulphuric Acid by Contact process
We will first start by addressing the question of what is sulphuric acid. Well, sulphuric acid is basically an oxidizing agent, a strong mineral acid, and a dehydrating agent. Sulphuric acid has the chemical formula H2SO4.
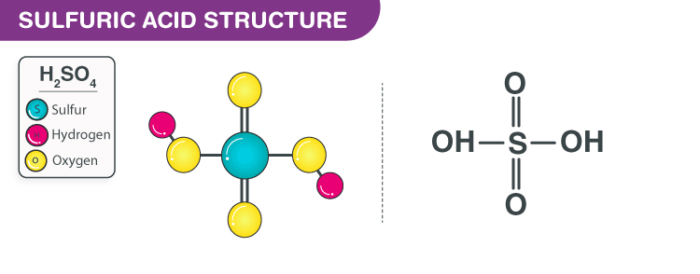
The acid is a colourless liquid. It is soluble in water and generally releases heat on contact. Further, the acid is corrosive in nature to metals and tissues. It will even char wood and most other organic matter on contact, but chances of objects catching fire are null. The acid has a density of 15 lb/gal. Exposure to the acid can result in adverse health effects from inhalation. It depends on the rate of exposure and concentration.

Sulphuric Acid 3D ball Structure
That being said, the acid is usually manufactured using a method known as the contact process. Earlier, in this process, a chemical element known as platinum was first used as a catalyst. Later, an inorganic compound known as vanadium oxide replaced platinum due to cost constraints.
In any case, today we will be looking at the contact process in detail.
Contact process for manufacturing of sulphuric acid:
Steps involved in the manufacturing of sulphuric acid are as stated below:
Preparation of sulphur dioxide.
Conversion of sulphur dioxide into sulphur trioxide.
Conversion of sulphur trioxide formed into concentrated H2SO4.
Step 1: Preparation of sulphur dioxide:
SO2 is prepared by burning sulphur in the presence of excess air so that the product combines with oxygen which is helpful for the next stage.
S(s) + O2 (g) → SO2(g)
Step 2: Preparation of sulphur trioxide:
Sulphur trioxide is formed when sulphur dioxide reacts with oxygen in a ratio of 1:1 at a temperature of 400 °C – 450°C and a pressure of 1-2 atm in the presence of V2O5 as a catalyst. This reaction is reversible in nature.
2SO2(g) + O2(g) ⇌ 2SO3(g)
Step 3: Preparation of concentrated sulphuric acid:
The sulphur trioxide formed is first made to react with concentrated sulphuric acid. Sulphur trioxide cannot be dissolved in water directly as it leads to the formation of fog. The product obtained after this reaction is known as oleum. The oleum obtained is then dissolved in water to obtain concentrated sulphuric acid.
H2SO4 + SO3(g) → H2S2O7(l)
H2S2O7(l) + H2O(l) → 2H2SO4
Uses of Sulphuric Acid
In Industries:
Up to 50 per cent of this liquid manufactured is used in the production of phosphoric acid which is in turn used to make phosphate fertilizers.
It is used in the manufacturing of metals such as copper, zinc etc.
5 per cent of the produced acid is used in the making of fibres.
In Domestic Environments:
Used in acidic drain cleaners.
Due to its strong dehydrating property, it can be used to remove the tissue paper.
As a Catalyst:
Used as a catalyst in the manufacturing process of nylon.
Used in the Manheim process in the manufacturing of HCl.
Used in petroleum refining.
Frequently Asked Questions
How Sulphuric acid is produced?
Sulphuric acid is produced from sulphur. In the presence of air, sulphur dioxide is first obtained by burning the molten sulphur. In the presence of a catalyst for vanadium pentoxide, sulphur dioxide is then converted to sulphur trioxide.
What type of acid is sulphuric acid H2SO4?
Sulphuric acid is a powerful mineral acid that at all concentrations is soluble in water. Sulphuric acid contains two atoms of hydrogen, one atom of sulphur, and four atoms of oxygen. Sulphuric acid H2SO4- A colourless to dark brown liquid that is highly corrosive.
What is the pH of Sulphuric acid?
Because sulphuric acid is a strong acid, a sulphuric acid solution of 0.50 M has a pH near zero.
Will sulphuric acid dissolve metal?
Aluminum, which is a highly reactive metal, will not dissolve in oxidizing acids (e.g. nitric), as it will grow on its surface a protective layer of aluminum oxide. Thallium, for example, dissolves in sulphuric acid, but not in hydrochloric acid.
Is H2SO4 a Monoprotic acid?
The monoprotic acid is hydrobromic acid because only one proton (H) can be given. No monoprotic hydrogen exists. There are two acid protons in the starting acid, sulphuric acid (H2SO4). In other words, the sulfate molecule was bound to these acidic protons.